How To Become A Nurse In 2024? 6 Key Steps
Are you passionate about making a difference in people's lives? Do you have a strong desire to help others and provide compassionate care? If so, pursuing a career in nursing might be the perfect path for you. As we step into the year 2024, nursing jobs continue to evolve and expand, offering numerous opportunities for aspiring nurses. In this blog post, we will explore the essential steps you need to see how to become a nurse in 2024.
What does a nurse do?
Nurses play a crucial role in the healthcare system, providing care, support, and advocating for patients. Here are some key responsibilities and tasks that nurses typically perform:
1- Patient care
Assessing and monitoring patients' health conditions.
Administering medications, treatments, and procedures prescribed by physicians.
Providing wound care, injections, and intravenous therapy.
Assisting with activities of daily living, such as bathing, dressing, and feeding.
Educating patients and their families about health conditions, medications, and self-care.
2- Collaboration with healthcare team
Collaborating with physicians, therapists, and other healthcare professionals to develop and implement patient care plans.
Communicating and coordinating patient care with interdisciplinary team members.
Participating in rounds and patient care conferences to discuss treatment plans and progress.
3- Patient advocacy
Acting as a liaison between patients, their families, and the healthcare system.
Advocating for patients' rights and ensuring their needs are met.
Providing emotional support and compassionate care to patients and their families.
4- Documentation and record-keeping
Accurately documenting patient information, including medical history, symptoms, and treatment plans.
Recording vital signs, medication administration, and other relevant data.
Maintaining electronic health records and ensuring confidentiality.
5- Health promotion and education
Promoting health and preventing illness through patient education and health promotion initiatives.
Teaching patients about disease prevention, healthy lifestyle choices, and self-care techniques.
Collaborating with community organizations to promote public health initiatives.
6- Emergency response
Responding to emergencies and providing immediate care in crisis situations.
Performing life-saving interventions such as cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and first aid.
7- Research and quality improvement
Participating in research studies to advance nursing knowledge and improve patient care outcomes.
Contributing to quality improvement initiatives to enhance healthcare practices and patient safety.
8- Leadership and management
Taking on leadership roles within healthcare organizations or nursing teams.
Supervising and delegating tasks to other healthcare personnel.
Contributing to policy development and implementation.
Nurses work in a variety of healthcare settings, including hospitals, clinics, nursing homes, schools, and community health centers. Their dedication and expertise make them essential members of the healthcare team, ensuring that patients receive the highest quality of care and support throughout their healthcare journey.
Steps to becoming a nurse
The following section outlines the essential steps to transform an interest in becoming a nurse into a rewarding career. It covers various aspects, including selecting a suitable nursing program and eventually finding a job.
1- Education requirements to become a nurse
To become a registered nurse (RN), there are four main paths: earning a diploma from an accredited nursing program, obtaining an associate degree in nursing (ADN), or obtaining a bachelor's degree in nursing (BSN), or master of science in nursing (MSN).
The following programs provide a comprehensive understanding of nursing, covering essential subjects such as anatomy, physiology, psychology, microbiology, and behavioral sciences. Currently, the most common pathway to start a nursing career is through an associate degree program, although bachelor's degrees are increasingly popular. Below is a brief overview of the three routes available to become a nurse:
Diploma in Nursing (24 months)
Although few hospitals offer diploma programs, they were once a popular option. These programs involve nursing courses at the hospital and general education courses at a local college. However, they are becoming less available as associate degree programs offer a similar curriculum with additional advantages, such as better employment prospects.
Associate Degree in Nursing (typically 24 months)
An associate degree is the standard requirement for registered nurses today. Due to the shorter duration, it is a popular choice as it allows aspiring nurses to obtain their license and enter the field more quickly. These programs combine classroom instruction with clinical experiences to provide a solid foundation for a nursing career.
Bachelor's Degree in Nursing (typically 4 years)
With employers increasingly valuing well-educated nurses, a Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) degree offers an advantage in the job market. Around 80 percent of employers prefer hiring BSN graduates. A BSN also opens doors to management positions and further education opportunities. Students can pursue a traditional four-year bachelor's program or obtain an associate degree and RN licensure, later returning for a BSN through flexible or online RN-to-BSN programs.
These programs should meet the requirements for taking the mandatory nursing licensing examination, but it is crucial to consult your state's board of nursing or your nursing school for specific education requirements in your state.
Master of Science in Nursing (2-3 years)
The Master of Science in Nursing (MSN) is an advanced nursing degree. Typically, applicants are required to have a Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) before enrolling in an MSN program. Many MSN programs offer online options and provide flexibility for students to study either part-time or full-time. One notable aspect of this degree is its versatility. Depending on individual goals, the MSN can serve various purposes. Students in this program can choose to enhance their general nursing knowledge and skills, specialize in specific areas of nursing, or explore education, leadership, or business aspects. Additionally, at the graduate level, students have the opportunity to pursue an MSN and become a nurse practitioner. This flexibility in choosing a focus area is valuable for individuals aiming to achieve specific career objectives.
When considering whether to pursue an MSN, it is important to have a clear career goal in mind. Additionally, understanding the entry requirements of the desired program is crucial. Generally, these programs require a BSN, a nursing license, and a minimum GPA.
2- Obtain a license
As previously mentioned, obtaining a nursing license through the successful completion of a national nursing licensure examination (NCLEX) is crucial for nurses to practice their profession. The specific requirements for licensure vary depending on the state, nursing specialty, and occupation. Most nursing programs have administrative departments that can offer guidance on obtaining the appropriate licensure, but it is important to understand which examination is relevant to your situation. Here are three commonly known national exams:
Certified Nursing Assistant (CNA)
This state-specific competency exam is designed for individuals seeking to work as nursing assistants. The CNA role involves a limited scope of responsibilities, and the exam will reflect that focus.
National Council Licensure Examination for Practical Nurses (NCLEX-PN)
Licensed Practical Nurses (LPNs) are required to pass this exam. LPNs have a broader range of responsibilities compared to CNAs. They are involved in administering certain medications and conducting specific medical tests. The NCLEX-PN exam covers these additional responsibilities and assesses comprehension of fundamental healthcare assistance.
National Council Licensure Examination for Registered Nurses (NCLEX-RN)
Registered Nurses (RNs) are required to pass this comprehensive exam in order to practice. Among the three exams mentioned, the NCLEX-RN is the most extensive, as it assesses a broader range of nursing knowledge and skills.
It is important to be aware of the specific exam that aligns with your nursing career aspirations and to prepare accordingly.
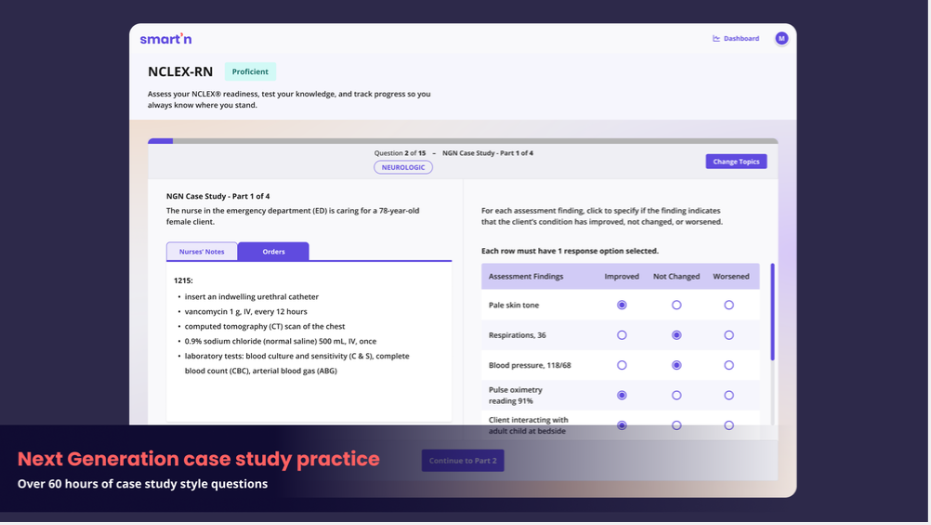
If you need help in the process of passing your NCLEX exam, you can take advantage of a quality NCLEX study tool like Smart’n.
Smart'n is a platform designed to support nursing students in their studies by providing access to a wide range of practice questions, rationales, and assessments.
With over 2,500 practice questions and 60+ hours of NGN NCLEX-style nursing case studies available on Smart'n, students can find NextGen questions and case studies that are concise and categorized by topic. This makes it easier to focus on specific areas of nursing practice, such as respiratory, cardiac, mental health, neurological, and more.
To access the NGN case studies on Smart'n, you need to upgrade your free account. You can also access additional resources and content that are specifically geared towards case studies, helping you to gain a deeper understanding of complex nursing scenarios.
One of the key features of Smart'n is its personalized quizzes. These quizzes are tailored to the individual needs of each student and generated by the platform's AI based on recommended topics for practice. This allows students to focus on areas where they may need more practice or review, helping them to strengthen their knowledge and skills.
Additionally, Smart'n provides ongoing assessments and a clear overview of their performance, allowing students to gauge their progress and identify areas of strength and weakness. This feedback can be invaluable in helping students to target their studies and focus on areas that may require further attention.
3- Consider state requirements
Each state has its own requirements for nursing licensure. It's important to check the specific requirements of the state in which you intend to practice and fulfill any additional requirements, such as criminal background checks or fingerprinting.
4- Decide which type of nurse you want to be
Nursing offers various career paths, ranging from starting as a certified nursing assistant (CNA) or staff nurse and progressing to roles like nurse administrator.
When deciding on your career trajectory, it's important to consider the work environment that suits you best. Registered nurses (RNs) can be found in hospitals, doctor's offices, and other medical settings, whereas certified nursing assistants often work in nursing homes. Reflect on the type of setting that inspires you the most.
Additionally, think about the role you aspire to fulfill. If you prefer being part of a team that supports medical staff, a CNA or licensed practical nurse/licensed vocational nurse (LPN/LVN) role might be suitable. However, if you desire to manage other nurses and assistants or oversee systems, a career as an RN or advanced practice nurse would likely be a better fit.
Given the diverse aspects of healthcare, nurses often specialize in specific areas such as geriatrics or critical care. If you have a particular passion for a certain type of nursing, it is essential to consider the educational requirements necessary to pursue that specialization.
5- Obtain employment
Once you have completed your education and obtained the necessary license, the next step is to secure a job in the nursing field. Fortunately, nursing is experiencing rapid growth, with a projected 15% increase in employment opportunities by 2026, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). This growth rate is more than double the average national rate for all occupations. It is worth noting that nursing has also become a popular profession, resulting in healthy competition for available positions.
The likelihood of finding employment can be influenced by factors such as location and specific areas of nursing. For example, as the population ages, long-term care facilities are expected to gain popularity, leading to an increased demand for registered nurses (RNs) in those settings. Additionally, regions with well-established medical communities often offer exciting new opportunities. Cities like New York City and Philadelphia, along with their surrounding suburbs, boast excellent hospitals and successful universities that offer top-notch nursing degree programs.
6- Continue education
Nursing is a dynamic field, and ongoing professional development is essential. Engage in continuing education opportunities to stay updated on the latest advancements, research, and best practices in nursing.
While not essential for everyone, pursuing further education can be a valuable option for individuals with specific career aspirations. In the nursing field, like other professions, advanced degrees often lead to senior-level positions, increased salaries, and greater responsibilities. The good news is that there are numerous options available for advanced nursing degrees. Consider exploring GMercyU's Master of Science in Nursing and Doctor of Nursing Practice programs for more information.
Types of nurses
After acquiring the necessary educational qualifications, students have the option to select from a diverse range of nursing specialties. The specific roles and responsibilities of nurses may vary based on the healthcare industry's demands and the preferences of the individuals. Presented below are some examples of job profiles within the nursing profession.
1- Registered Nurse (RN)
RNs are the most common type of nurses. They provide direct patient care, assess patient needs, develop care plans, administer medications, and educate patients and their families about various health conditions.
2- Licensed Practical Nurse (LPN)
LPNs work under the supervision of RNs or physicians. They provide basic nursing care, such as taking vital signs, administering medications, and assisting with patient hygiene. LPNs often work in long-term care facilities or clinics.
3- Nurse Practitioner (NP)
NPs are advanced practice registered nurses (APRNs) who have obtained a master's or doctoral degree in nursing. They diagnose and treat illnesses, order and interpret diagnostic tests, prescribe medications, and provide primary care services. NPs may specialize in areas such as family medicine, pediatrics, or mental health.
4- Certified Nurse Midwife (CNM)
CNMs are APRNs specializing in women's health and providing prenatal, childbirth, and postnatal care. They assist with labor and delivery, offer family planning services, and provide gynecological care. CNMs often work in hospitals, birthing centers, or private practices.
5- Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetist (CRNA)
CRNAs are APRNs who administer anesthesia during surgical procedures. They monitor patients' vital signs, manage pain relief during and after surgery, and ensure safe anesthesia administration. CRNAs work in collaboration with surgeons, anesthesiologists, and other healthcare professionals.
6- Pediatric Nurse
Pediatric nurses specialize in caring for infants, children, and adolescents. They provide comprehensive healthcare services, including immunizations, well-child exams, and treatment of common childhood illnesses.
7- Geriatric Nurse
Geriatric nurses specialize in caring for elderly patients. They address age-related health concerns, manage chronic conditions, provide end-of-life care, and promote overall well-being in older adults.
8- School Nurse
A school nurse is a registered nurse who works in a school and takes care of students' health needs. They provide basic medical care, administer medications, conduct health screenings, and promote overall wellness.
9- Aesthetic/Cosmetic Nurse
An aesthetic/cosmetic nurse is a registered nurse who specializes in providing cosmetic treatments and procedures to enhance the appearance of individuals. These nurses typically work in aesthetic clinics, medical spas, or plastic surgery centers. They are trained and skilled in performing non-surgical aesthetic procedures such as Botox injections, dermal fillers, laser treatments, chemical peels, and other cosmetic treatments. Aesthetic/cosmetic nurses often work closely with plastic surgeons, dermatologists, or other healthcare professionals to help patients achieve their desired aesthetic goals. They may also provide pre- and post-operative care, patient education, and assist in surgical procedures in some cases.
10- Travel Nurse
A travel nurse is a registered nurse who works on a temporary basis in various healthcare facilities or locations. Unlike nurses who have a permanent position in a specific hospital or clinic, travel nurses are employed by travel nurse agencies and are assigned to different assignments that typically last for 13 weeks, although the duration can vary.
11- Neonatal (NICU) Nurse
A neonatal (NICU) nurse is a registered nurse who specializes in providing medical care and support to newborn infants, particularly those who are premature, critically ill, or have other health complications. NICU stands for Neonatal Intensive Care Unit, which is a specialized unit within a hospital where these infants receive specialized care.
12- Labor and Delivery Nurse
A labor and delivery nurse is a registered nurse who specializes in providing care and support to women during the childbirth process. They work in labor and delivery units within hospitals or birthing centers, assisting women during labor, delivery, and immediately after childbirth.
13- Flight Nurse
A flight nurse is a registered nurse who is specially trained to provide medical care to patients during air transport. Flight nurses work on medical evacuation flights, often aboard helicopters or fixed-wing aircraft, to transport patients from one healthcare facility to another. They are part of a critical care transport team that includes pilots, paramedics, and other healthcare professionals.
14- Psychiatric Nurse
A psychiatric nurse, also known as a mental health nurse, is a registered nurse with specialized training and experience in providing care for individuals with mental health disorders. They work in a variety of settings, including psychiatric hospitals, mental health clinics, community health centers, and other healthcare facilities.
15- Forensic Nurse
A forensic nurse is a registered nurse who specializes in providing healthcare services to individuals involved in legal or criminal justice systems. They have a unique combination of nursing skills and forensic science knowledge, allowing them to work with victims of crime, suspects, and individuals within correctional facilities.
16- Nurse Anesthetist
A nurse anesthetist, also known as a Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetist (CRNA), is an advanced practice registered nurse (APRN) who specializes in providing anesthesia care to patients. They are highly trained healthcare professionals who work closely with surgeons, anesthesiologists, and other members of the healthcare team to ensure the safe administration of anesthesia during medical procedures.
17- Hospice Nurse
A hospice nurse, also known as a palliative care nurse, is a registered nurse (RN) who specializes in providing care and support to patients who are in the final stages of a terminal illness or nearing the end of their lives. Hospice care focuses on improving the quality of life for patients and their families by addressing their physical, emotional, and spiritual needs.
18- Legal Nurse Consultant (LNC)
A legal nurse consultant (LNC) is a registered nurse (RN) who utilizes their medical expertise and knowledge to provide consultation and support to attorneys, legal teams, insurance companies, and other organizations involved in legal cases that involve medical issues. They bridge the gap between the medical and legal fields by providing valuable insights, analysis, and interpretation of medical records and healthcare-related issues.
19- Scrub Nurse
A scrub nurse, also known as a surgical nurse or operating room nurse, is a specialized registered nurse who works directly within the sterile field during surgical procedures. They are an integral part of the surgical team and play a crucial role in ensuring patient safety and surgical efficiency.
20- Surgical Nurse
A surgical nurse, also known as an operating room nurse or perioperative nurse, is a registered nurse (RN) who specializes in providing care to patients before, during, and after surgical procedures. They work closely with the surgical team to ensure the safety and well-being of patients throughout the surgical experience.
21- Wound Care Nurse
A wound care nurse, also known as a wound care specialist or wound care nurse consultant, is a registered nurse (RN) who specializes in the assessment, treatment, and management of various types of wounds. They have expertise in wound healing, infection control, and the use of specialized wound care products and techniques.
22- Nurse Assistant
A nurse assistant, also known as a nursing assistant, certified nursing assistant (CNA), or patient care assistant (PCA), is a healthcare professional who provides direct patient care under the supervision of registered nurses (RNs) or licensed practical nurses (LPNs). They work in various healthcare settings, such as hospitals, nursing homes, assisted living facilities, and home healthcare agencies.
23- Nurse Educator
A nurse educator is a registered nurse (RN) who has specialized knowledge and experience in teaching and educating future nurses, current nursing students, and practicing nurses. They play a critical role in the development and enhancement of nursing education, ensuring that nurses have the necessary knowledge and skills to provide safe and effective patient care.
24- Nurse Recruiter
A nurse recruiter is a professional who specializes in recruiting and hiring nurses for healthcare organizations, such as hospitals, clinics, nursing homes, and other healthcare facilities. They play a crucial role in attracting and selecting qualified nurses to meet the staffing needs of the organization.
25- Sane Nurse
A SANE nurse, also known as a Sexual Assault Nurse Examiner, is a registered nurse who has undergone specialized training to provide comprehensive care to victims of sexual assault or abuse. SANE nurses play a critical role in providing compassionate and sensitive care while collecting forensic evidence and ensuring the physical and emotional well-being of the survivor.
26- Public Health Nurse
A public health nurse is a registered nurse (RN) who specializes in public health and works to promote and protect the health of populations or communities. They focus on preventing illness, promoting healthy behaviors, and improving access to healthcare services.
27- Nurse Informatics
A nurse informatics, also known as a Nursing Informatics Specialist or Nurse Informaticist, is a registered nurse who specializes in the field of nursing informatics. Nursing informatics is a specialty that combines nursing science, computer science, and information science to manage and communicate data, information, knowledge, and wisdom in nursing practice.
28- Trauma Nurse
A trauma nurse, also known as an emergency or critical care nurse, is a registered nurse (RN) who specializes in providing care for patients who have experienced severe injuries or critical illnesses. These nurses work in various healthcare settings, including emergency departments, trauma centers, intensive care units (ICUs), and other acute care facilities.
Trauma nurses are highly skilled and trained to assess, stabilize, and manage patients with life-threatening conditions. They are responsible for providing immediate care to patients who have suffered severe injuries, such as those resulting from accidents, gunshot wounds, falls, or other traumatic incidents. They work closely with physicians, surgeons, and other members of the healthcare team to provide comprehensive and specialized care to patients in critical situations.
29- Clinical Nurse Specialist
A clinical nurse specialist (CNS) is an advanced practice registered nurse (APRN) who has acquired specialized knowledge and expertise in a specific area of nursing practice. A clinical nurse specialist's role involves direct patient care, education, research, and consultation.
Clinical nurse specialists typically hold a master's or doctoral degree in nursing and have extensive clinical experience in their chosen specialty. They work in various healthcare settings, including hospitals, clinics, long-term care facilities, and community health centers.
30- Family Nurse Practitioner
A family nurse practitioner (FNP) is an advanced practice registered nurse (APRN) who specializes in providing primary healthcare services to individuals and families across the lifespan. FNPs are trained to diagnose and manage common acute and chronic illnesses, promote wellness, and provide preventive care.
31- Dermatology Nurse
A dermatology nurse is a registered nurse who specializes in providing care to patients with various skin conditions and diseases. They work under the supervision of dermatologists and collaborate with other healthcare professionals to deliver comprehensive dermatological care.
32- Military Nurse
A military nurse is a registered nurse who serves in the armed forces and provides healthcare services to military personnel, their families, and sometimes to civilian populations during humanitarian missions. Military nurses work in various branches of the military, such as the Army, Navy, Air Force, and Coast Guard.
33- Botox Nurse
A Botox nurse is a registered nurse who specializes in administering Botox injections for cosmetic purposes. Botox, short for Botulinum Toxin, is a neurotoxic protein that is used in small, diluted amounts for cosmetic treatments to temporarily reduce the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines.
34- Mental Health Nurse
A mental health nurse is a registered nurse who specializes in providing care and support to individuals with mental health disorders and psychiatric conditions. Mental health nurses work in various settings, including psychiatric hospitals, outpatient clinics, community health centers, correctional facilities, and residential treatment programs.
35- Holistic Nurse
A holistic nurse is a registered nurse who embraces a holistic approach to nursing care, focusing on the integration of physical, mental, emotional, and spiritual aspects of an individual's well-being. Holistic nursing recognizes the interconnectedness of these dimensions and seeks to promote health and healing in a comprehensive and balanced way.
36- Nurse Administrator
A nurse administrator is a registered nurse who takes on a leadership role in healthcare organizations and oversees and manages various aspects of nursing and patient care services. Nurse administrators may work in hospitals, clinics, long-term care facilities, public health agencies, or other healthcare settings.
37- Obgyn Nurse
An OB/GYN nurse, also known as an obstetric-gynecologic nurse or simply a women's health nurse, is a registered nurse who specializes in providing care to women throughout their lifespan, with a particular focus on reproductive health, pregnancy, childbirth, and gynecological care. OB/GYN nurses work in various healthcare settings, including hospitals, clinics, private practices, and women's health centers.
38- Nurse Case Manager
A nurse case manager is a registered nurse who specializes in coordinating and managing the care of patients across various healthcare settings. They work closely with patients, healthcare providers, and insurance companies to ensure the effective and efficient delivery of healthcare services.
39- Vet Nurse
A vet nurse, also known as a veterinary nurse or veterinary technician, is a trained professional who provides medical and nursing care to animals under the supervision of a veterinarian. Vet nurses work in veterinary clinics, animal hospitals, research facilities, animal shelters, and other veterinary settings.
40- Baby Nurse
A "baby nurse" is a colloquial term that can refer to two different types of professionals who provide care for newborn infants and their families:
Neonatal Nurse: A neonatal nurse is a registered nurse who specializes in caring for newborn infants, particularly those who are premature, critically ill, or have medical complications. Neonatal nurses work in neonatal intensive care units (NICUs) and other specialized settings. They monitor the baby's vital signs, administer medications, provide developmental care, educate parents on newborn care, and offer support during the infant's hospital stay.
Newborn Care Specialist: A newborn care specialist, also known as a baby nurse or infant care specialist, is a non-medical professional who provides specialized care for newborns in their homes. These individuals typically have extensive experience and training in newborn care and offer services such as feeding support, sleep guidance, diaper changing, soothing techniques, and general infant care. They may also provide guidance and education to parents on newborn care practices.
It's important to note that the term "baby nurse" can be used interchangeably and may vary in its specific meaning depending on the context and region.
41- Fertility Nurse
A fertility nurse, also known as a reproductive nurse or infertility nurse, is a registered nurse who specializes in providing care and support to individuals and couples undergoing fertility treatments and assisted reproductive technologies (ART). Fertility nurses work closely with fertility specialists and reproductive endocrinologists in fertility clinics, reproductive medicine centers, and assisted reproduction facilities.
What skills do I need to be a nurse?
To be a nurse, you need a combination of technical skills, medical knowledge, and personal qualities. Here are some key skills and qualities that are important for a nursing career:
1- Medical knowledge
Nurses should have a solid understanding of anatomy, physiology, pharmacology, and other medical concepts. This knowledge forms the foundation for providing safe and effective patient care.
2- Clinical skills
Nurses need to develop practical clinical skills, such as administering medications, wound care, monitoring vital signs, performing basic medical procedures, and using medical equipment. These skills are crucial for providing direct patient care and responding to emergencies.
3- Communication skills
Effective communication is essential in nursing. Nurses must be able to listen actively, ask questions, and provide clear instructions to patients, their families, and other healthcare professionals. Good communication helps to establish trust, gather accurate information, and provide emotional support.
4- Critical thinking
Nurses should possess strong critical thinking skills to assess patient conditions, analyze information, and make quick and sound decisions. They must be able to prioritize tasks, anticipate potential complications, and take appropriate action in dynamic healthcare environments.
5- Empathy and compassion
Nursing involves caring for people who are often vulnerable and going through challenging times. Empathy and compassion are essential qualities that allow nurses to connect with patients, provide emotional support, and advocate for their needs.
7- Adaptability
The healthcare field is ever-evolving, and nurses must be adaptable to new technologies, procedures, and treatment methods. They should be open to learning and willing to embrace change as healthcare practices advance.
8- Organizational skills
Nurses often juggle multiple responsibilities, including managing patient records, administering medications, coordinating care plans, and collaborating with other healthcare professionals. Strong organizational skills are necessary to stay organized, manage time effectively, and ensure patient safety.
9- Teamwork and collaboration
Nurses work closely with other healthcare professionals, including doctors, therapists, and support staff. The ability to collaborate effectively as part of a team is crucial for delivering comprehensive and coordinated care.
10- Emotional resilience
Nursing can be emotionally demanding, as nurses may encounter stressful situations, suffering, and loss. Emotional resilience is important to maintain composure, cope with challenging circumstances, and provide support to patients and their families.
11- Ethical and professional conduct
Nurses must adhere to ethical standards, maintain patient confidentiality, and uphold professional conduct at all times. They should demonstrate integrity, honesty, and a commitment to the well-being of their patients.
Remember, these skills and qualities can be further developed and refined through education, training, and practical experience. Nursing is a rewarding and diverse profession, and ongoing learning is essential for professional growth and providing the best possible care to patients.
Conclusion
In conclusion, becoming a nurse in 2024 requires a combination of technical skills, medical knowledge, and personal qualities. The nursing profession continues to evolve, and aspiring nurses must be prepared to adapt to new technologies and advancements in healthcare. However, the core attributes of a successful nurse remain unchanged: empathy, compassion, critical thinking, and effective communication.
FAQs
1- How many years does it take to get a nurse?
The length of time it takes to become a nurse can vary depending on the educational path you choose. Here are the typical pathways and their corresponding timeframes:
Licensed Practical Nurse (LPN) or Licensed Vocational Nurse (LVN): This is the shortest nursing program, usually taking around 1 year to complete.
Registered Nurse (RN) - Associate Degree in Nursing (ADN): ADN programs generally take about 2 to 3 years to complete.
Registered Nurse (RN) - Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN): BSN programs typically require 4 years of study at a college or university.
Registered Nurse (RN) - Accelerated BSN Programs: These programs are designed for individuals who already hold a bachelor's degree in a different field. Accelerated BSN programs usually last around 12 to 18 months and provide an intensive nursing curriculum.
2- What skills do you need to be a nurse?
Here are 10 skills required to be a nurse:
Medical Knowledge
Clinical Skills
Communication Skills
Critical Thinking
Empathy and Compassion
Adaptability
Organizational Skills
Teamwork and Collaboration
Emotional Resilience
Ethical and Professional Conduct